Understanding Autogenous Training: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Autogenous Training?
Autogenous training, often recognized as a self-hypnosis or relaxation method, focuses on achieving a state of deep relaxation and self-awareness. Developed by physician Johannes Heinrich Schultz in the early 20th century, this technique aims to induce a calming effect on the mind and body. Employing techniques such as visual imagery or repetition of calming phrases, individuals learn to control their physiological responses to stress. **Autogenous training** is widely used in various settings, including enhancing performance in athletes, managing stress in daily life, and contributing to pain relief in medical contexts.

The Principles of Autogenous Training
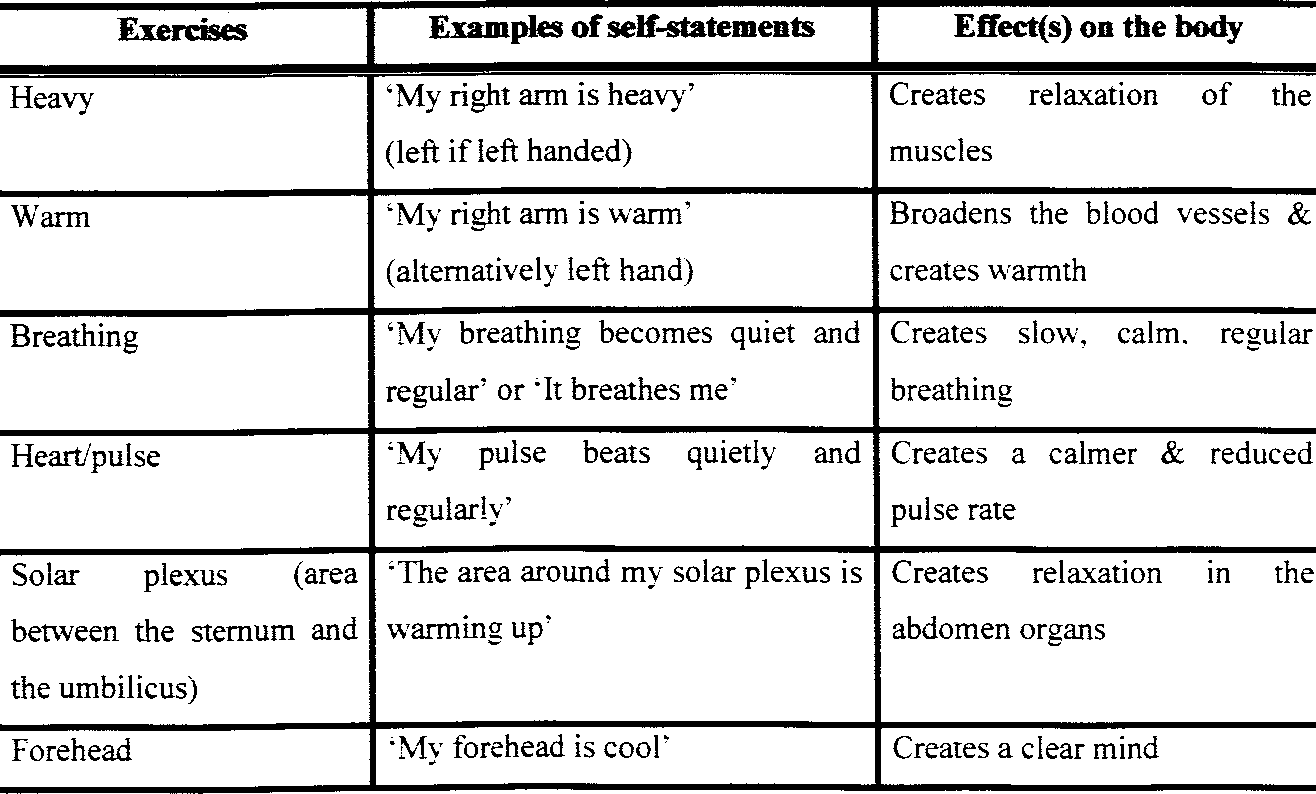
The fundamental principles of **autogenous training** revolve around inducing relaxation through self-suggestion. The process typically includes six main exercises that help participants develop a sense of warmth and heaviness in their bodies. These sensations are closely associated with physical relaxation and a decrease in tension. During these exercises, individuals can deepen their mental focus, allowing a shift into a more serene mental state. Regular practice not only facilitates relaxation responses but also fosters long-term benefits like improved concentration and emotional balance.
Benefits of Autogenous Training
Engaging in autogenous training offers numerous **benefits for mental health and well-being**. It can significantly reduce levels of everyday stress and anxiety, providing individuals with tools to manage challenging emotions effectively. Furthermore, consistent practice enhances self-confidence and resilience, empowering individuals to handle life’s challenges with greater ease. Studies suggest that those who practice autogenous training report more significant improvements in coping mechanisms, better sleep quality, and elevated overall mood. As a holistic approach, this technique encourages personal growth and self-discovery.
How to Practice Autogenous Training
Practicing autogenous training primarily involves a structured routine that individuals can adapt according to their personal schedules. To begin, choose a quiet space where distractions are minimized. Sit or lie down comfortably, and engage in 5-10 minutes of guided breathing to promote relaxation. After achieving a gentle state of calm, you can start visualizing calming images or repeating affirmations that correspond to each exercise of warmth and heaviness in your limbs. Regular practice helps reinforce these associations, enhancing your ability to evoke these sensations at will.

Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
For those new to **autogenous training**, these step-by-step guidelines will help lay a solid foundation for your practice:
- Find a Quiet Location: Seek out a serene environment where you can focus without interruptions.
- Get Comfortable: Position yourself comfortably, whether sitting or lying down. This relaxation is crucial for effectiveness.
- Breathe Deeply: Start with deep, calming breaths to lower your heart rate and prepare your mind.
- Use Affirmations: Gradually repeat phrases like “My arms are heavy” or visualize warmth spreading through your body.
- Practice Regularly: Aim to practice daily or several times a week to build your skills and deepen your relaxation responses over time.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While autogenous training can bring substantial benefits, beginners may encounter certain challenges. A common issue is difficulty maintaining focus or getting distracted during exercises. To address this, consider incorporating calming background music or guided audiobooks during the practice to enhance concentration. Furthermore, consistency might be challenging; thus, scheduling your practice like a daily appointment can create a dedicated habit that ensures persistence. With time and regular practice, the challenges will diminish as your proficiency improves.
Applications of Autogenous Training
The applications of autogenous training extend far beyond personal relaxation practices. It is used effectively within sports psychology to help athletes manage pre-competition nerves and enhance performance. By preparing mentally, athletes can focus on their objectives, reducing anxiety that may hinder their potential. In clinical settings, autogenous training is frequently employed as part of treatment protocols for anxiety disorders, chronic pain relief, and even some cardiovascular issues, offering patients a complementary tool to support their conventional therapies.
Autogenous Training for Stress Management
In a fast-paced world, **stress management** is vital for maintaining well-being. Autogenous training caters to individuals dealing with heightened stress due to personal or professional challenges. By integrating this practice into daily life, people can significantly reduce their stress levels and promote an overall sense of tranquility. Techniques learned through autogenous training not only aid in acute stress situations but also build resilience over time, creating a mental buffer against future stressors. Regular practice empowers individuals to approach stress with a calmer mindset, improving their emotional health.
Case Studies of Successful Implementation
Several studies highlight the positive impacts of **autogenous training** on diverse populations, including college students, corporate employees, and patients with anxiety disorders. For example, implementing a six-week **autogenous training program** among college students resulted in noticeable reductions in anxiety levels and improved academic performance. Another study involving corporate workers revealed that daily practice fell to greater work satisfaction and emotional resilience. These case studies underline the flexibility of autogenous training across different contexts, showcasing its effectiveness when tailored to meet unique individual needs.
Key Takeaways
- **Autogenous training** promotes deep relaxation and mental clarity through self-suggestion techniques.
- Practicing regularly offers diverse benefits, such as stress reduction and improved emotional balance.
- Implementing a structured practice routine fosters skill acquisition and enhances emotional resilience.
- Applications of autogenous training encompass improvements in sports, personal stress management, and therapeutic settings.
FAQ
1. What are the main exercises of autogenous training?
The primary exercises in **autogenous training** include the overall feeling of heaviness and warmth at various body parts, such as arms, legs, and the heartbeat meditation. These exercises promote relaxation by enhancing body awareness and encouraging a tranquil state. Completing these exercises regularly can lead to a deeper understanding of your body and further instill relaxation techniques.
2. How long does it take to see results from autogenous training?
While individual experiences may vary, most people notice improvements within a few weeks of consistent practice. Starting with just 5-10 minutes daily can generate observable different outcomes, including enhanced relaxation and greater stress management abilities. Results tend to compound as you deepen your practice.
3. Can children practice autogenous training?
Yes, children can practice autogenous training with appropriate language and guidance. Teaching children to visualize calming scenarios or repeat simple affirmations can help them manage anxiety, promote focus, and enhance their overall emotional regulation, making it a valuable tool for students and young athletes alike.
4. Is autogenous training a substitute for medical help?
While **autogenous training** can be a helpful complement to treating various conditions, it should not replace medical care or therapy if needed. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals regarding mental health concerns, while simultaneously incorporating autogenous training as an additional support mechanism.
5. What should I do if I struggle with self-suggestion during practice?
If self-suggestion proves challenging, consider utilizing guided recordings or apps designed for relaxation. These resources can provide affirmations and comfort, assisting you in entering a more profound state of relaxation. Over time, as you gain confidence, you may rely less on these external aids.